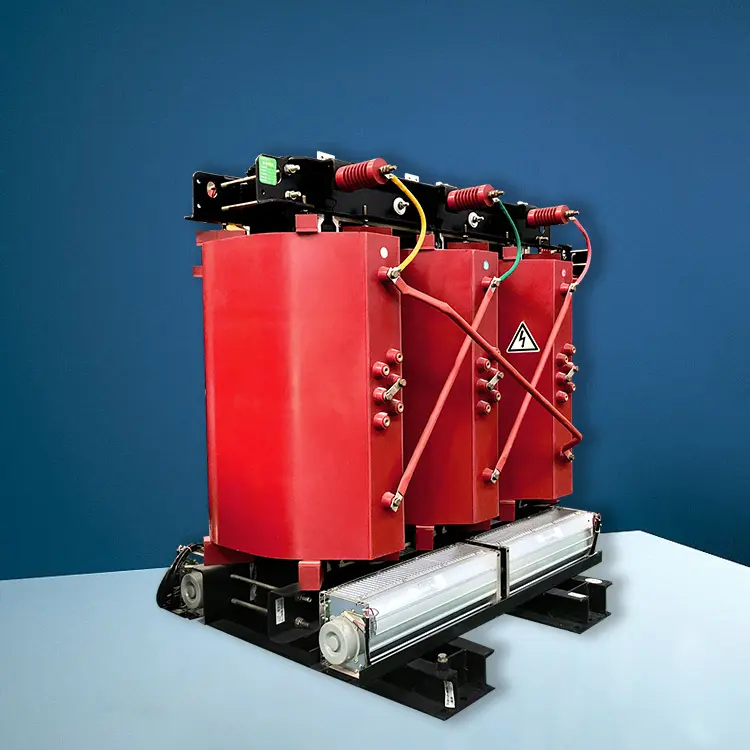
what is three-phase step-up transformer
A three-phase step-up transformer is a type of electrical transformer designed to increase the voltage level in a three-phase power system. Transformers are devices that transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction.such as those found in large buildings or industrial installations. This transformer increases the voltage level from the primary side (input) to the secondary side (output), hence the term “step-up”.
In a three-phase system, there are three conductors, usually labeled as phases, and the power is distributed evenly among them. The step-up transformer, as the name suggests, increases the voltage level from the input (primary) side to the output (secondary) side. This is commonly done for the purpose of long-distance power transmission, where higher voltages are more efficient for reducing energy losses during transmission.
The primary winding of the transformer is connected to the power source, and the secondary winding is connected to the load or the system that needs the higher voltage. The transformation ratio (turns ratio) determines the relationship between the primary and secondary voltages.
Three-phase step-up transformers play a crucial role in power distribution systems, helping to transmit electricity over long distances with reduced energy losses and improved efficiency.

Here’s how it works:
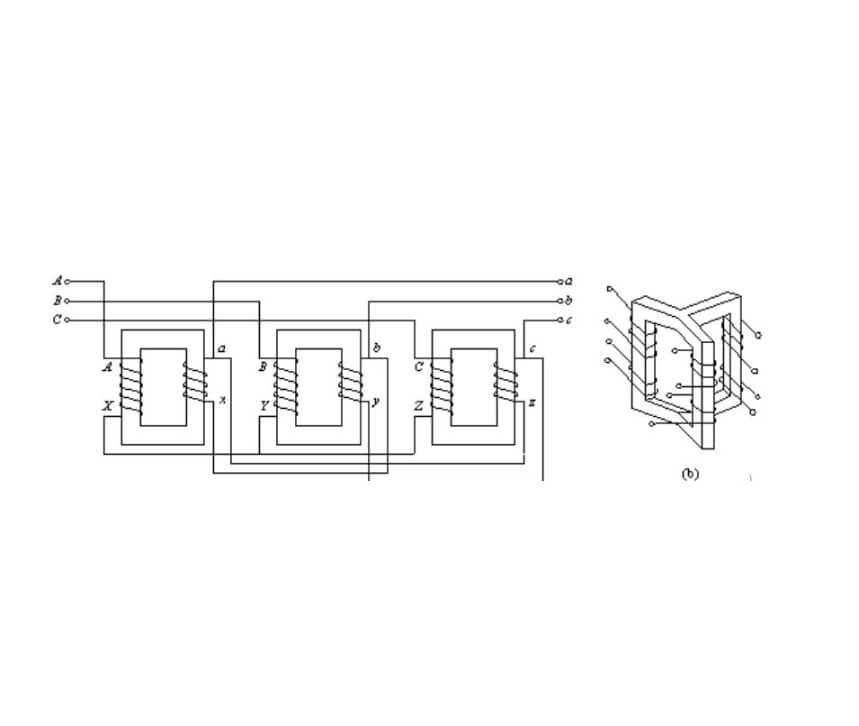
Input (Primary Side): The three-phase input power is connected to the primary windings of the transformer. These windings are usually connected in a delta or wye configuration.
Transformation: The transformer uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from the primary side to the secondary side. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding to the number of turns in the secondary winding determines the amount of voltage increase.
Output (Secondary Side): The stepped-up voltage is available at the secondary windings of the transformer. These windings can also be connected in a delta or wye configuration, depending on the requirements of the load.
To use a three-phase step-up transformer, you would connect the lower voltage (three-phase) supply to the primary side of the transformer, and the load that requires the higher voltage to the secondary side of the transformer. It’s important to ensure that the transformer is properly rated for the power that it needs to handle, and that all connections are made according to local electrical codes and standards. Always consult with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer when working with this type of equipment.

Tags:
Enameled Wire Copper wire Aluminum wire Enamelled wire Aluminum Winding Wire Magnet wire Modified polyester Round copper wire Heat resistance Enameled aluminum wire