single phase transformer
A single-phase transformer is a type of transformer that operates with a single-phase alternating current (AC) input. It consists of two coils of wire, the primary and secondary windings, which are wound around a common magnetic core. The primary winding is connected to the source of single-phase AC power, while the secondary winding is connected to the load.
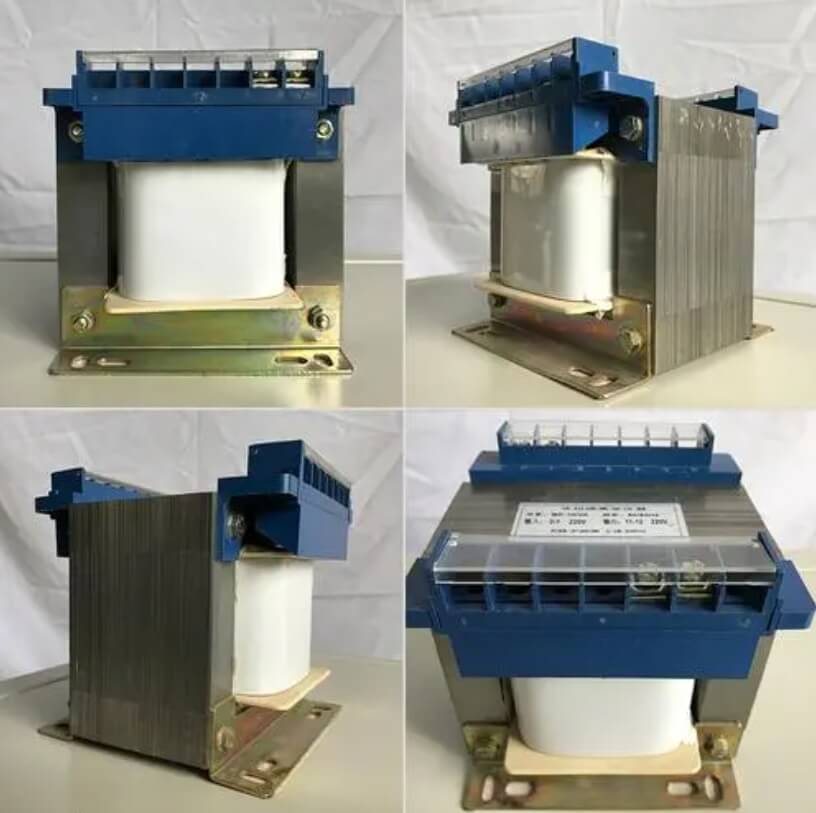

Single-Phase Transformers How They Work
- Electromagnetic Induction:
- When a single-phase alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding of the transformer, it produces a changing magnetic field around the winding. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
- Magnetic Core:
- The primary and secondary windings are wound around a common magnetic core, typically made of laminated iron or other magnetic materials. The core serves to efficiently transfer the magnetic flux generated by the current in the windings.
- Turns Ratio:
- The turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage transformation. If the secondary winding has more turns than the primary winding, it’s a step-up transformer (increasing voltage). If the secondary winding has fewer turns, it’s a step-down transformer (decreasing voltage).
- Transformer Equation:
- The product of the voltage and current in the primary winding equals the product of the voltage and current in the secondary winding for an ideal transformer.
- Efficiency and Losses:
- In practical applications, transformers experience some losses, including copper losses in the windings due to resistance and core losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. The efficiency of the transformer is the ratio of the power output to the power input.
- Applications:
- Single-phase transformers find use in a variety of applications, including power distribution, voltage regulation, and electrical devices. They are commonly employed in residential, commercial, and industrial settings where single-phase AC power is prevalent.
- Isolation and Safety:
- Transformers provide electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits, enhancing safety by preventing direct electrical connection. This isolation is crucial in many applications, especially in residential wiring and electronic devices.
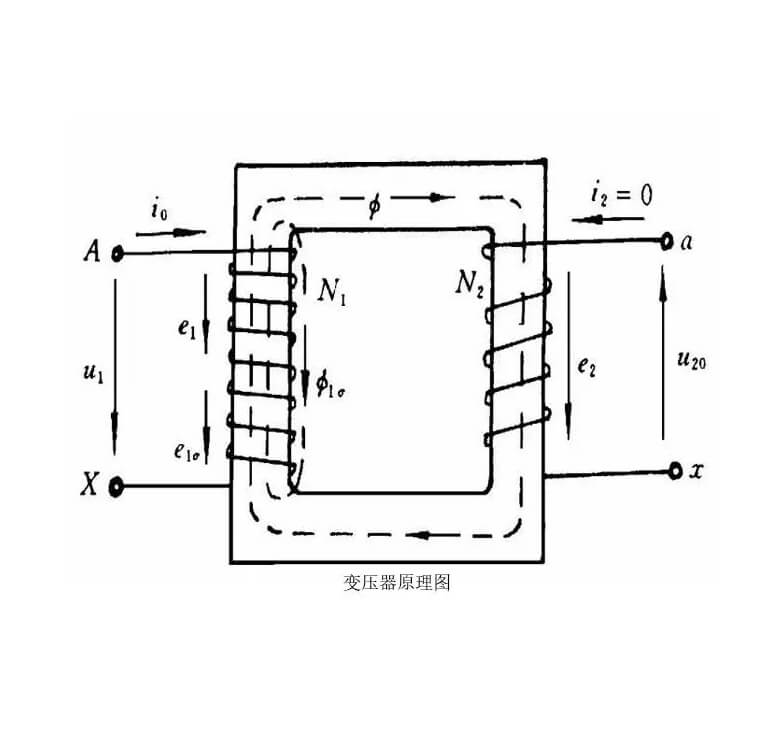
Key characteristics of a single-phase transformer include:
- Primary and Secondary Windings: The primary winding receives the input voltage from the single-phase AC source, generating a magnetic field around the core. The changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
- Voltage Transformation: The turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage transformation. If the secondary winding has more turns than the primary winding, it is a step-up transformer, increasing the voltage. If the secondary winding has fewer turns, it is a step-down transformer, decreasing the voltage.
- Transformer Equation: The relationship between the primary and secondary voltages and currents in an ideal single-phase transformer is described by the transformer equation: �primary⋅�primary=�secondary⋅�secondary.
- Applications: Single-phase transformers are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications where the power distribution system operates with single-phase AC. They are employed in various electrical devices, appliances, and equipment.
-
Efficiency and Power Factor: Like other transformers, single-phase transformers exhibit some losses, including copper losses in the windings and core losses. Their efficiency and power factor depend on factors such as design, load conditions, and quality of materials.
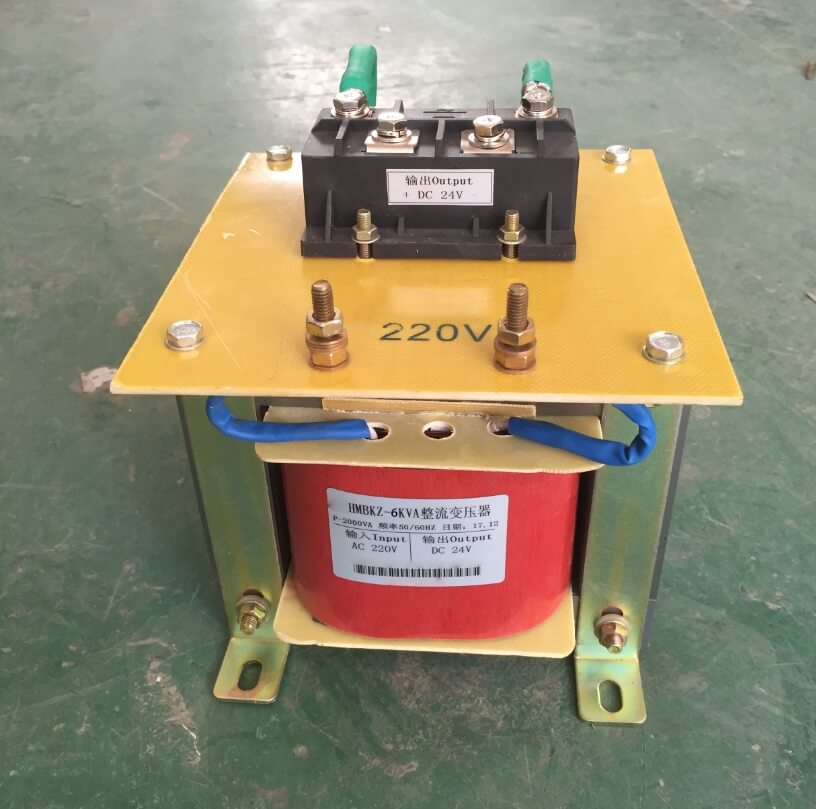

Single-phase transformers play a vital role in providing voltage regulation, adapting voltage levels for different applications, and facilitating the distribution of electrical power in systems that primarily use single-phase AC.

Tags:
Enameled Wire Copper wire Aluminum wire Enamelled wire Aluminum Winding Wire Magnet wire Modified polyester Round copper wire Heat resistance Enameled aluminum wire